What Causes White Gums After Whitening
Experiencing white gums after a teeth whitening procedure can be alarming, but it’s often a temporary issue. The primary cause of white gums is typically due to the whitening agents themselves. These agents, which often contain hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, are designed to bleach the enamel of your teeth. However, if these substances come into contact with your gum tissue, they can cause a reaction. Understanding the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. Furthermore, it is important to understand the difference between normal and dangerous white gums, so you should always consult with your dentist.
Chemical Burns From Whitening Products
The most common culprit behind white gums post-whitening is a chemical burn. This occurs when the bleaching agent comes into direct contact with the soft tissues of your gums. This contact can cause the gums to become irritated and appear white or blanched. The severity of the burn can vary depending on the concentration of the whitening agent, the duration of its exposure, and individual sensitivity. It’s important to note that while often temporary, chemical burns can be uncomfortable and may require attention.
How Whitening Products Affect the Gums

Whitening products work by penetrating the enamel of your teeth to break down the stains. However, the same process can affect the gums. The peroxide-based agents can strip away moisture from the gum tissue, leading to a whitening effect. The gums are sensitive and vulnerable, the products need time to be use and applied. Overuse or improper application can exacerbate the issue. The effect is similar to a mild burn, causing the surface cells to lose their color temporarily.
Signs of a Chemical Burn
Recognizing the signs of a chemical burn is important for prompt action. Apart from the white appearance, other symptoms include pain or stinging, redness, and swelling. The gums might also feel tender to the touch. In more severe cases, blisters or ulcers may develop. If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to rinse your mouth thoroughly with water and avoid further exposure to the whitening agent. Contacting your dentist for advice is also a good idea.
Professional Whitening vs. Over-the-Counter Products
The risk of white gums can vary depending on the type of whitening product used. Professional whitening treatments performed by a dentist typically involve higher concentrations of bleaching agents but also include protective measures like gum shields to minimize contact with the gum tissue. Over-the-counter products, such as whitening strips and trays, may have lower concentrations but can still cause irritation if not used correctly. Following the instructions carefully is paramount, regardless of the product. You should always consult with your dentist.
Other Causes of White Gums
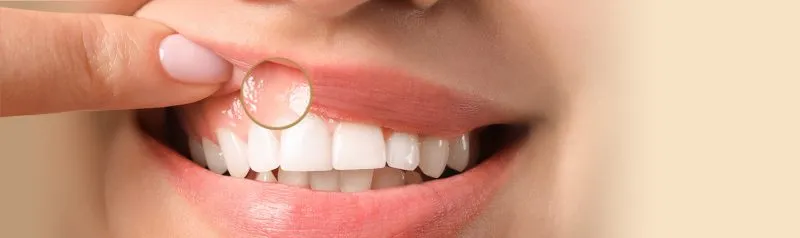
While chemical burns are the most common cause, other factors can contribute to white gums. These can range from simple dehydration to underlying health issues. Understanding these alternative causes can help you determine the best course of action and avoid unnecessary worry. If the whiteness persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, consulting a dental professional is advisable to rule out more serious conditions.
Dehydration and Its Effects on Gums
Dehydration can sometimes cause gums to appear white, especially if your mouth is dry. Insufficient water intake can lead to a lack of moisture in the tissues, causing them to look pale. Ensuring you stay hydrated, particularly after a whitening treatment, is crucial. Drinking plenty of water helps to rehydrate the gum tissue and can reduce the likelihood of white patches. Dry mouth can also increase the sensitivity of your gums.
Oral Infections and Gum Discoloration
In some cases, white gums can be a sign of an oral infection, such as thrush, which is caused by an overgrowth of yeast. Thrush can manifest as white patches or lesions on the gums, tongue, and inner cheeks. Other infections, like lichen planus, can also cause white, lacy patterns on the gums. If you notice white patches that are not related to whitening and are accompanied by other symptoms like pain, burning, or difficulty eating, it’s essential to see a dentist for diagnosis and treatment.
How to Prevent White Gums After Whitening
Preventing white gums is often easier than treating them. The key is to minimize exposure of the gums to whitening agents and practice good oral hygiene. Taking a proactive approach to protect your gums can save you discomfort and ensure the health of your smile. Proper preparation, careful application, and post-treatment care can make a significant difference in the outcome.
Choosing the Right Whitening Method
Choosing the right whitening method is crucial for minimizing the risk of white gums. Professional treatments offer more control and protection, as dentists can apply protective barriers to the gums before starting the procedure. If you opt for over-the-counter products, carefully read and follow all instructions. Consider using products with lower concentrations of whitening agents and shorter application times to reduce the risk of irritation. Always consult with your dentist before beginning any whitening treatment.
Importance of Professional Dental Care
Regular dental check-ups play a vital role in preventing and addressing issues like white gums. Dentists can identify potential problems early on and provide personalized recommendations for whitening treatments. They can also assess your overall oral health and suggest the most appropriate methods for your specific needs. Moreover, professional cleanings can remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can reduce sensitivity and improve the health of your gums. Maintaining a good relationship with your dentist is an investment in your oral health.
How to Treat White Gums

Treating white gums typically depends on the underlying cause and severity. In most cases, the condition resolves on its own within a few days as the gum tissue recovers. However, some measures can help to alleviate discomfort and promote healing. If you experience any unusual symptoms, such as persistent pain or bleeding, you should seek professional advice. The best treatment plan depends on the nature of the problem.
Home Remedies for Mild Cases
For mild cases of white gums caused by chemical burns, several home remedies can provide relief. Rinsing your mouth with water after whitening can help to remove any residual whitening agent. Applying a cold compress to your gums can reduce swelling and discomfort. Avoiding irritating foods and beverages, such as those that are acidic or spicy, can also help. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to manage pain. Be sure to follow up with your dentist.
When to See a Dentist
You should consult your dentist if white gums persist for more than a few days, or if you experience severe pain, swelling, or bleeding. Any signs of infection, such as fever or pus, should also prompt a visit to the dentist. If the white patches are accompanied by other symptoms, such as difficulty eating or swallowing, it’s important to seek professional help immediately. Your dentist can diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Maintaining Healthy Gums Post-Whitening

Maintaining healthy gums after a whitening treatment is crucial for long-term oral health. Proper care not only prevents complications like white gums but also ensures that your smile remains bright and healthy. The following practices can help you to keep your gums in the best possible condition and maintain the results of your whitening procedure. Consistent care is key to a beautiful and healthy smile.
Regular Dental Check-ups and Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for maintaining healthy gums. Your dentist can identify any early signs of gum disease or other problems and provide timely treatment. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar, which can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. These check-ups also allow the dentist to assess the effectiveness of your oral hygiene routine and provide personalized recommendations. Schedule regular visits to your dentist to keep your gums in top shape.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Practicing good oral hygiene is fundamental for preventing gum problems. Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacteria in your mouth. A healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and limiting sugary snacks and drinks can also contribute to healthy gums and a brighter smile. These habits will benefit your overall health.
